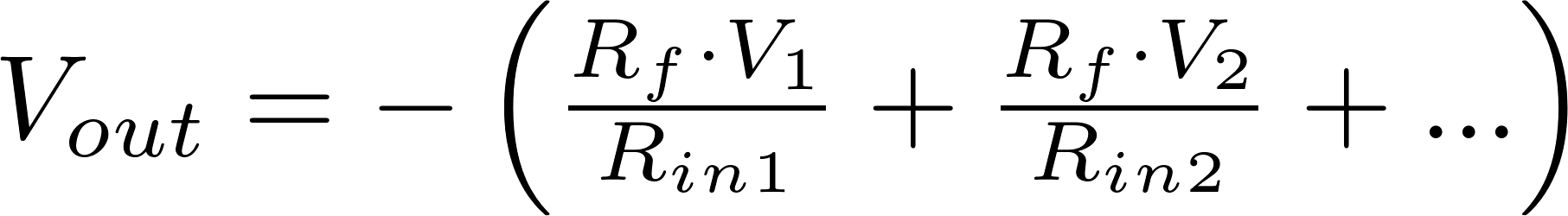Operational amplifier
An opamp is an amplifier with a very high gain and a differential input. The output voltage is often hundreds or even thousands of times larger than the voltage difference between the two inputs. The opamp has a non-inverting input (+) and an inverting input (-). The output voltage is an amplification of the voltage difference between the two inputs.
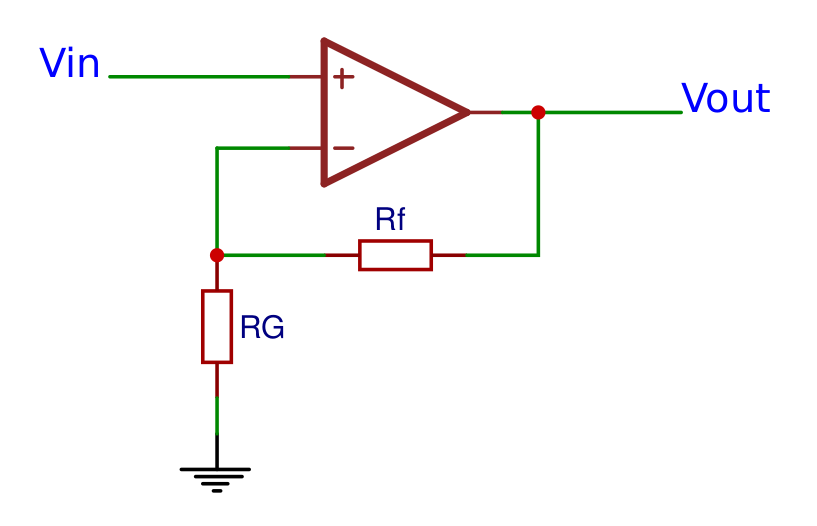
Non-inverting operational amplifier
Non inverting amplifierThe non-inverting opamp does not invert the input terminals, so the input voltage is connected to the positive terminal and the negative terminal is connected to ground. The output voltage can be calculated with the following formula:
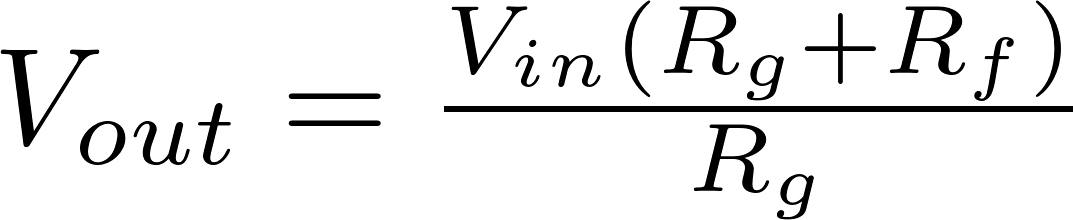
Inverting operational amplifier
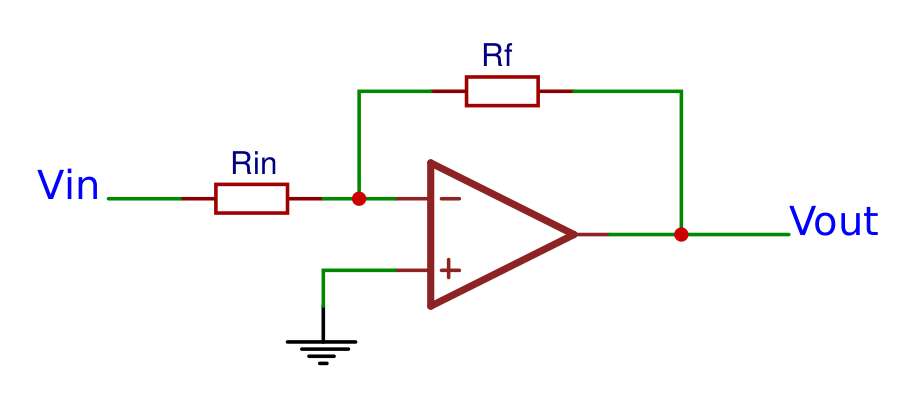
Inverting amplifierThe inverting opamp inverts the input terminals, so the input voltage is connected to the negative terminal and the positive terminal is connected to ground. If the input voltage is positive, the output voltage will be negative. The output voltage can be calculated with the following formula:
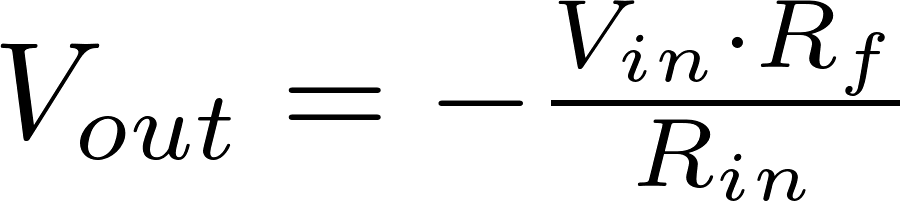
Differential operational amplifier
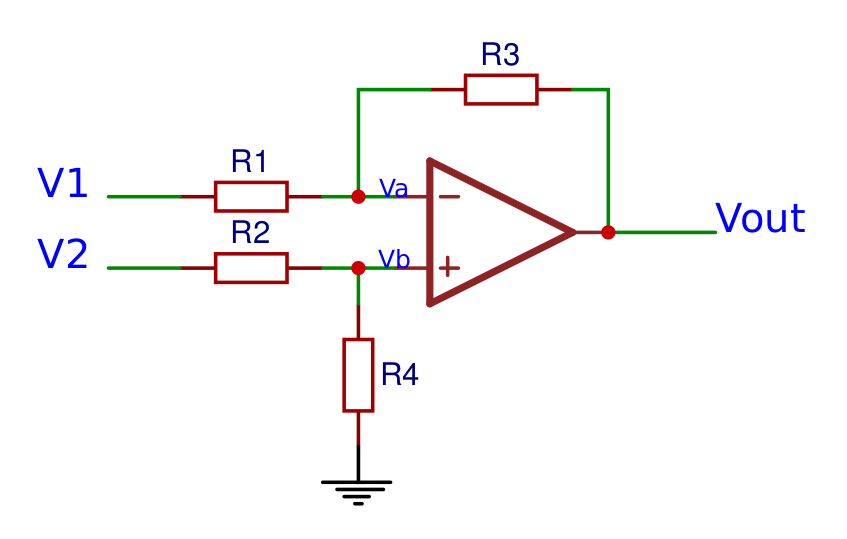
Differential amplifierThe differential opamp amplifies the difference between the two voltages. The output voltage can be calculated with the following formula:
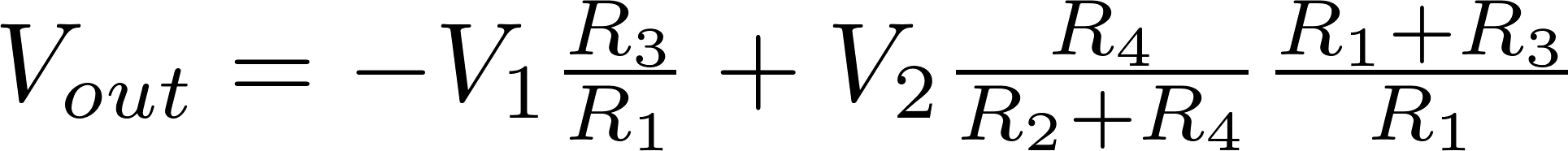
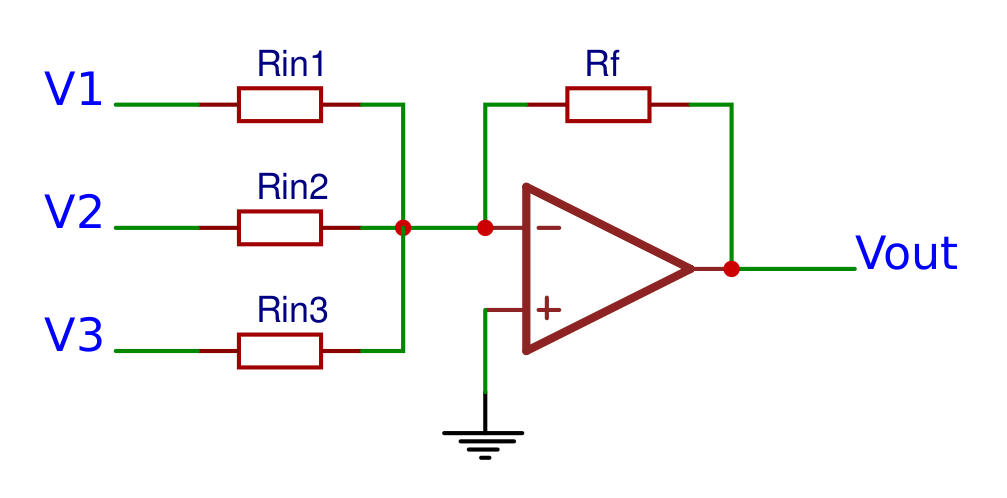
Inverting summing amplifier
Inverting summing amplifierThe inverting summing opamp works the same as the inverting opamp, so the input terminals are inverted and the input voltage is connected to the negative terminal and the positive terminal is connected to ground, but there are multiple input voltages connected to the negative terminal instead of only one. The output voltage can be calculated with the following formula: